csapp-chapter3-3.7-Procedures
CSAPP Chapter3 3.7 Procedures
概述
过程其实是软件中一种很重要的抽象。就像我们在写代码时,一个函数,传进去入参和一个可选的返回值定义了某个功能。不同的语言过程的形式多样,比如函数、方法、子例程、等等。
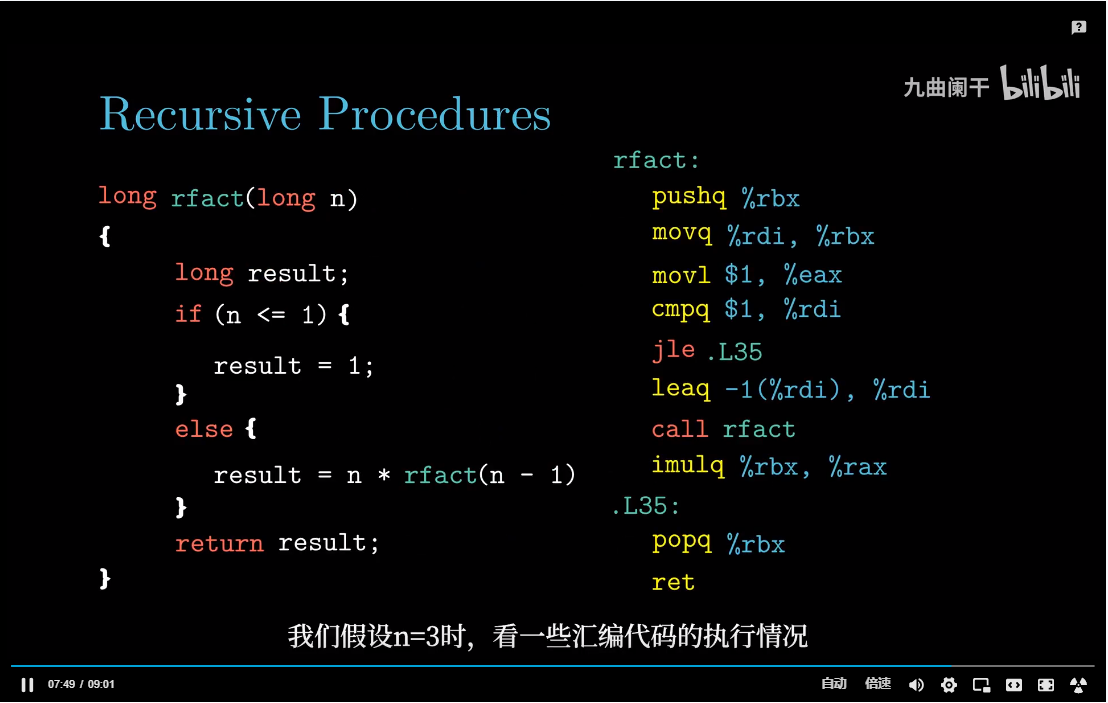
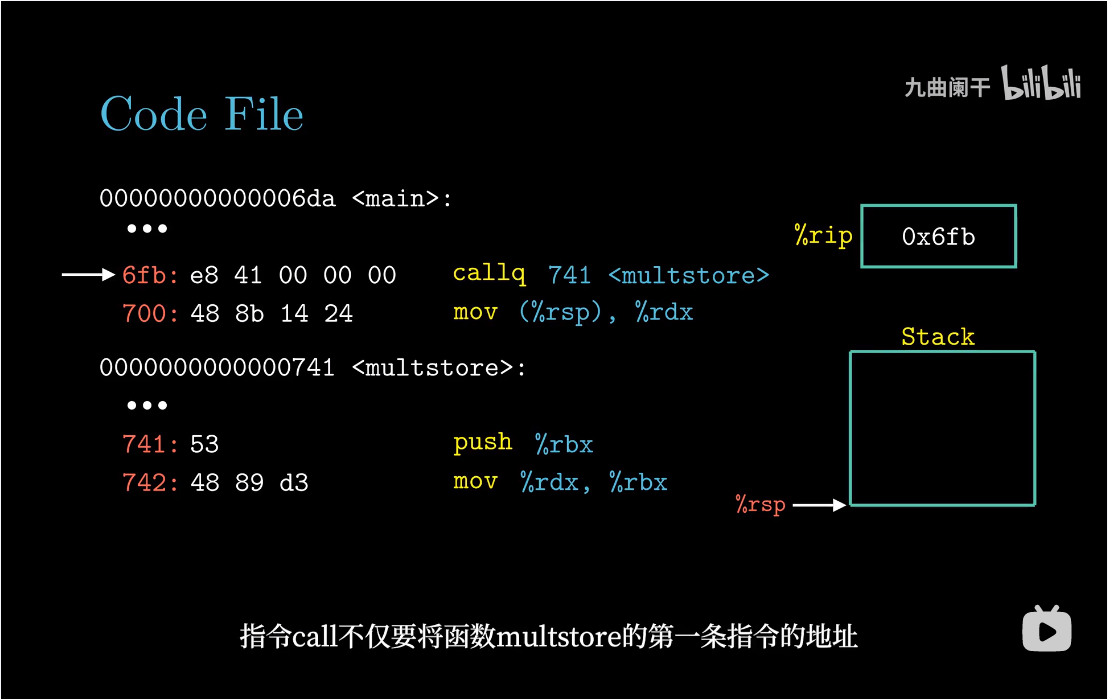
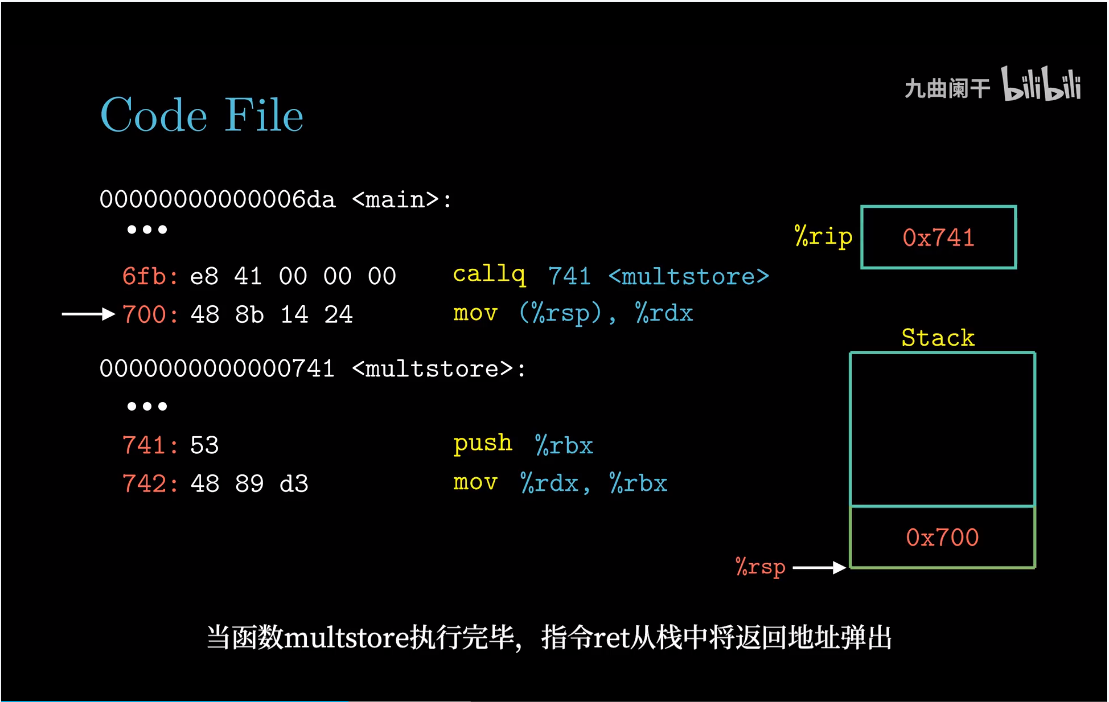
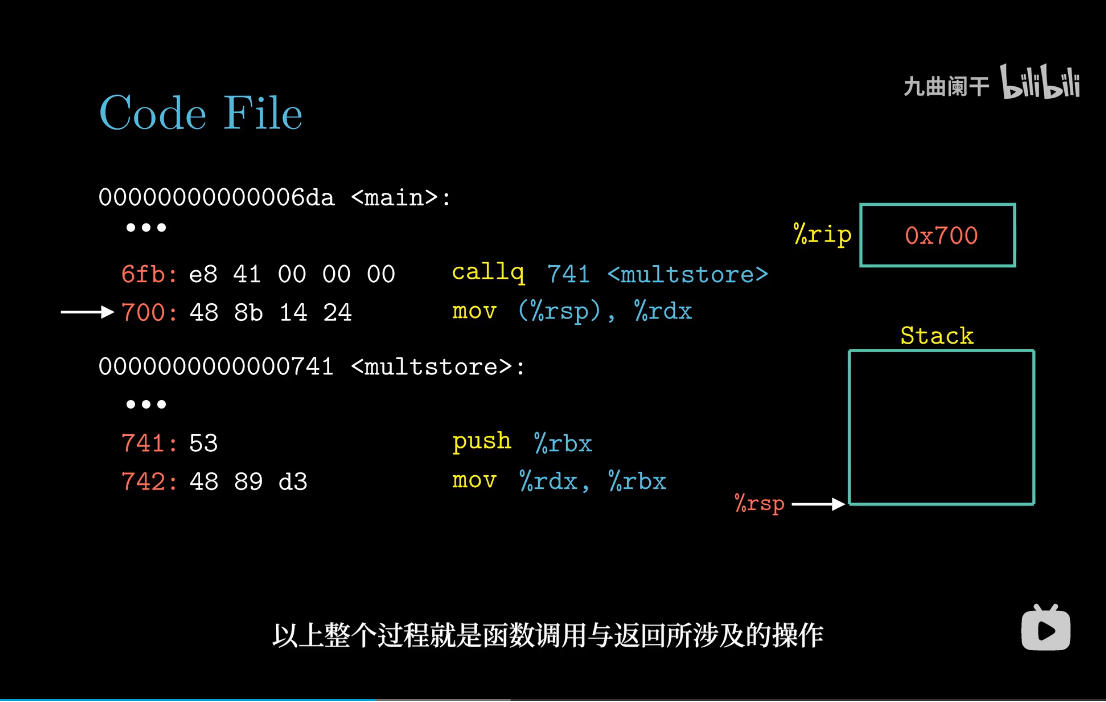
机器对过程的实现提供了下面几个支持,为了方便大家理解,例如:过程P调用过程Q,Q执行后返回到P,这些动作包含如下一个或多个机制:
传递控制。在进入Q时,PC要设置为Q代码的起始地址,然后在返回时,要设置为P调用Q后那条指令的地址;传递数据。P必须向Q提供一个或多个参数,Q必须向P提供一个返回值;分配和释放内存。Q在执行时需要为局部变量分配空间,当返回时,销毁这些空间;
演示代码
main.c
1 | |
mstore.c
1 | |
执行gcc命令, 生成可执行文件prog(windows平台该文件为prog.exe)
1 | |
文件变成了131k,因为它不仅包含了两个过程的代码,还包含了用来启动和终止程序的代码,以及用来和操作系统交互的代码
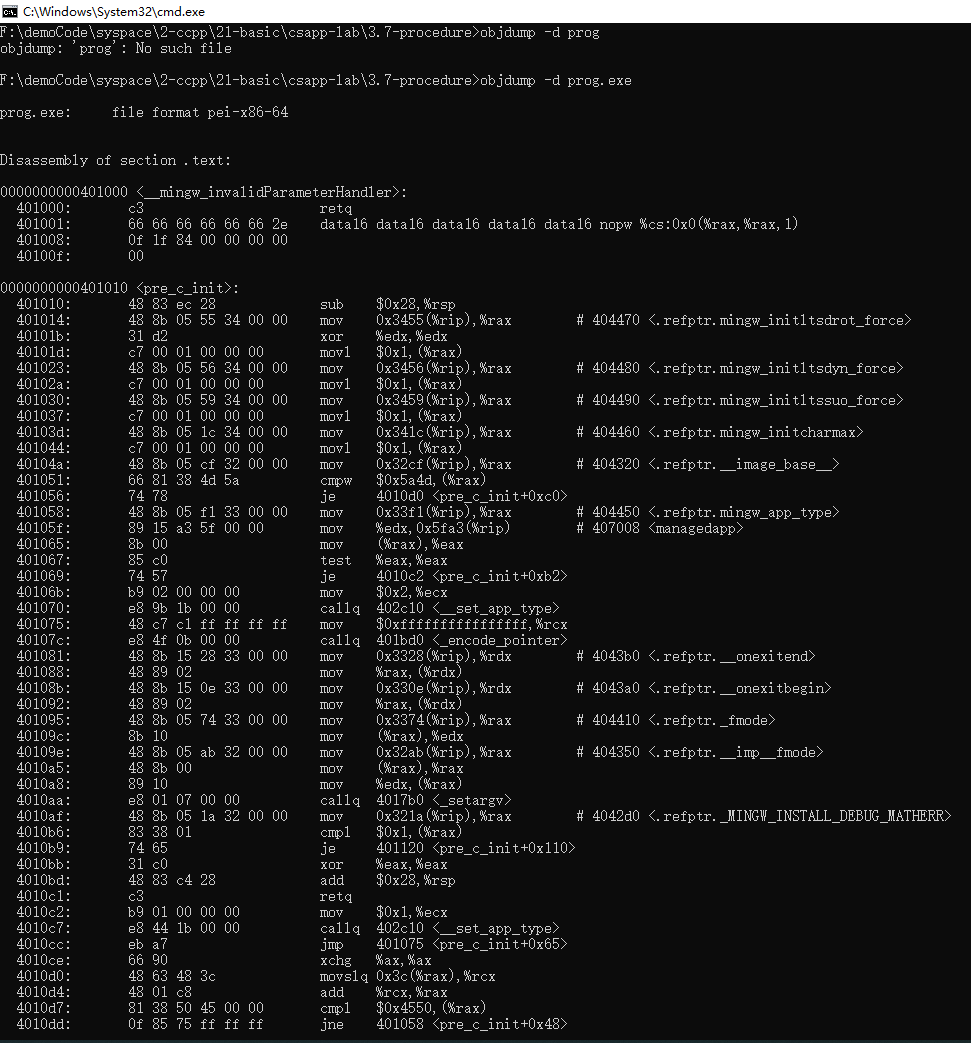
现在我们反汇编prog(windows平台该文件为prog.exe)文件:
linux平台
1 | |
windows平台
1 | |
NOTE:
3.10 Options That Control Optimization-Og
Optimize debugging experience. -Og enables optimizations that do not interfere with debugging. It should be the optimization level of choice for the standard edit-compile-debug cycle, offering a reasonable level of optimization while maintaining fast compilation and a good debugging experience.
If you use multiple -O options, with or without level numbers, the last such option is the one that is effective.
3.2 Options Controlling the Kind of Output
-o file
Place output in file file. This applies to whatever sort of output is being produced, whether it be an executable file, an object file, an assembler file or preprocessed C code.
If -o is not specified, the default is to put an executable file in a.out, the object file for source.suffix in source.o, its assembler file in source.s, a precompiled header file in source.suffix.gch, and all preprocessed C source on standard output.
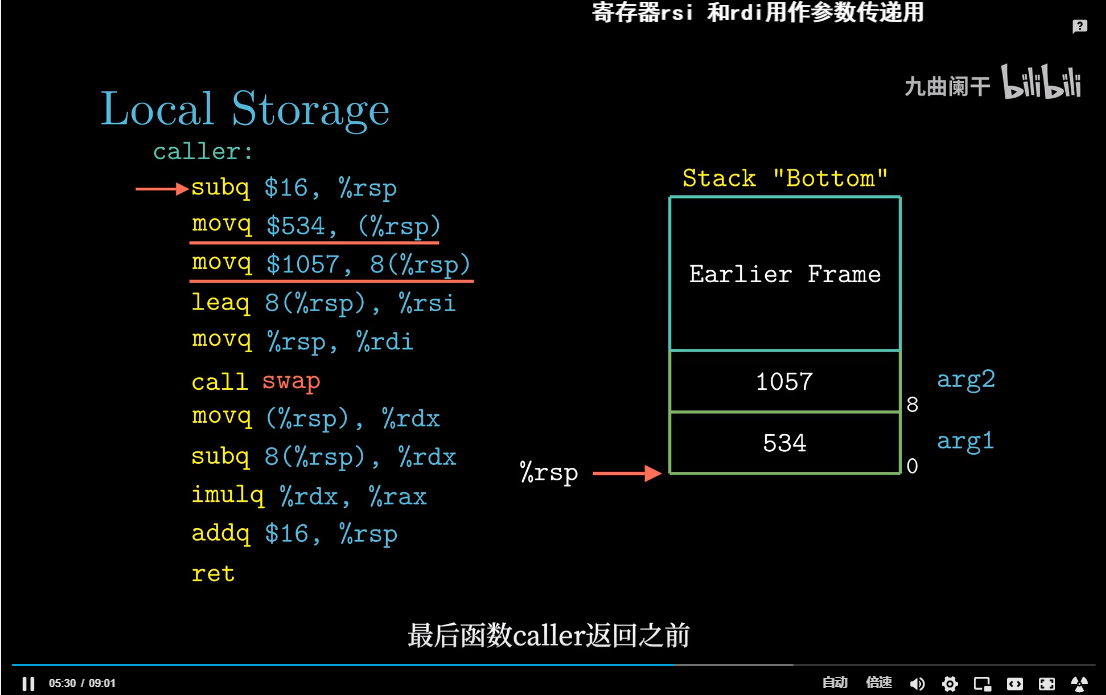
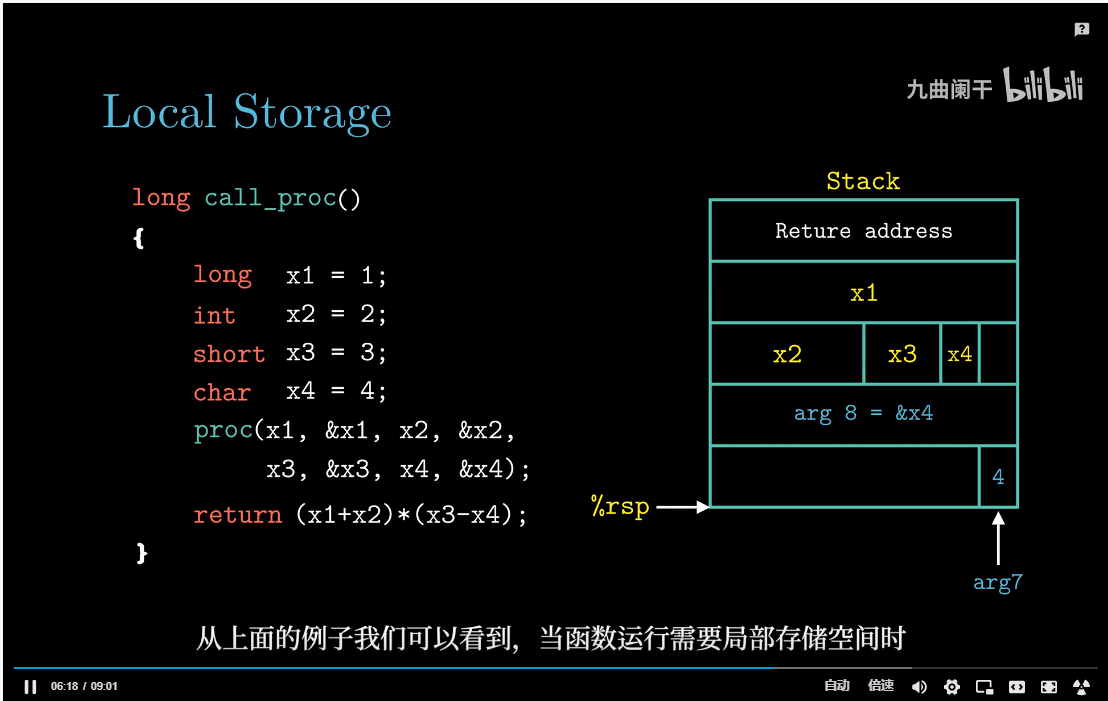
返回地址
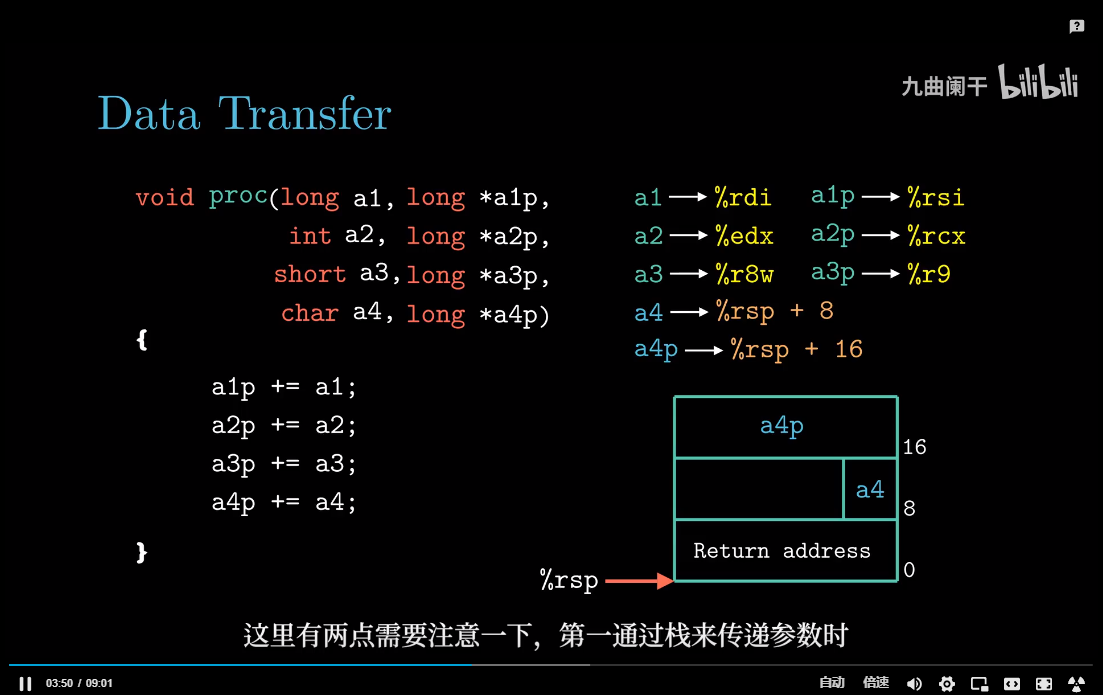
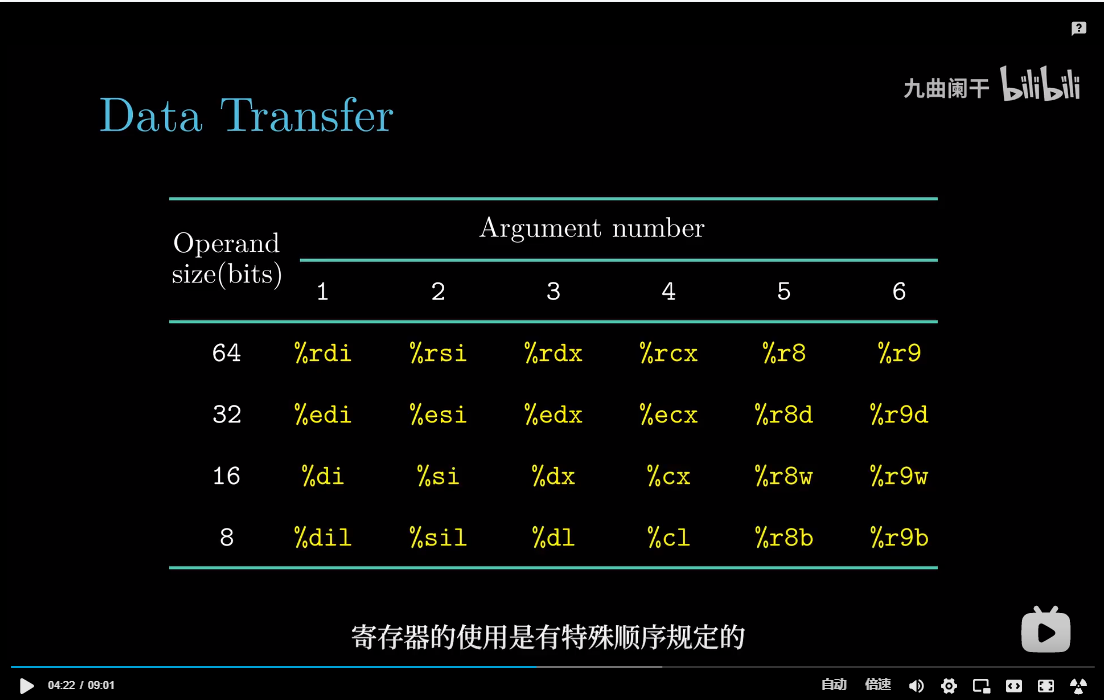
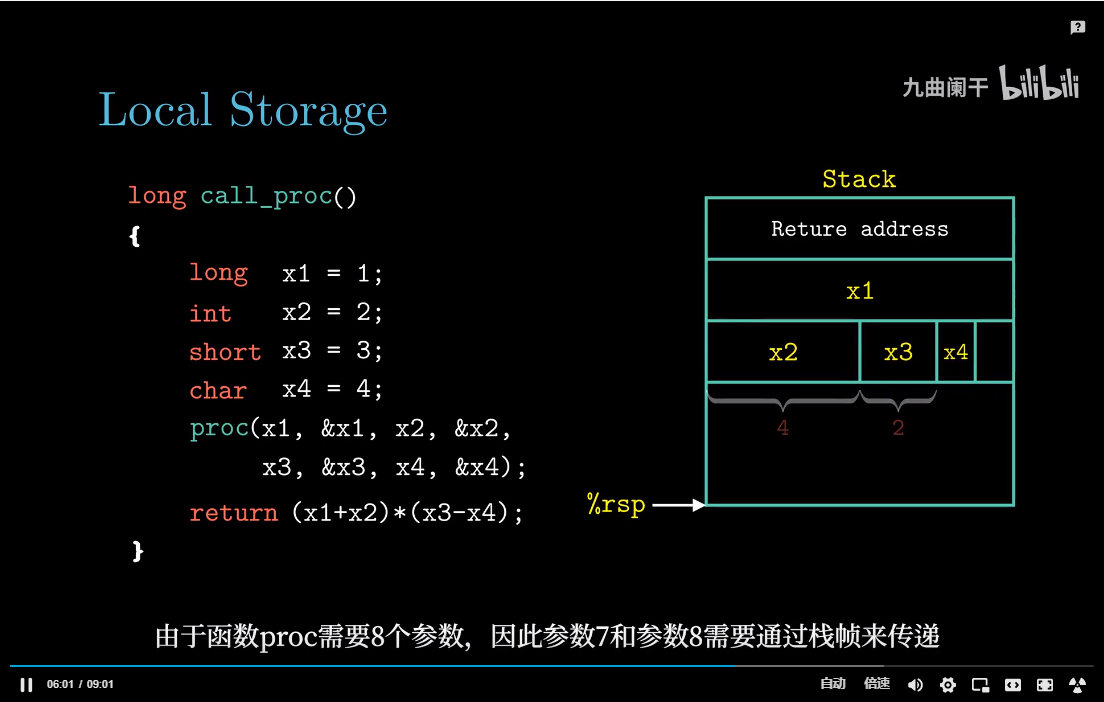
参数传递
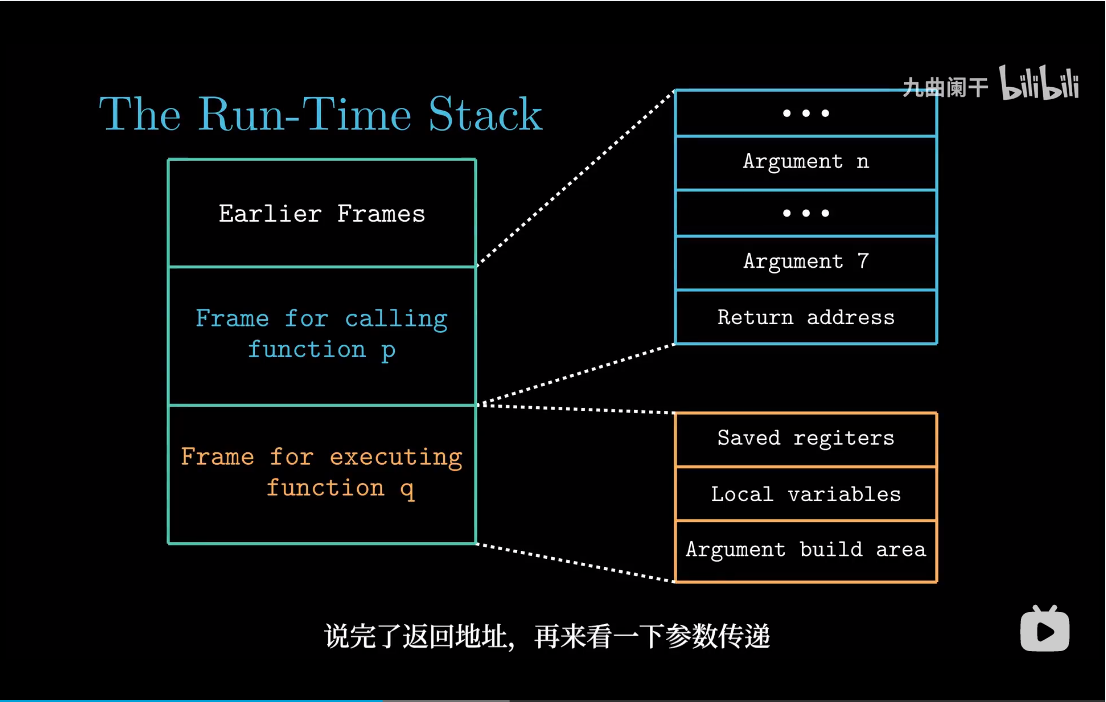
如果一个函数的参数数量大于6, 超出部分就要通过栈来传递。